
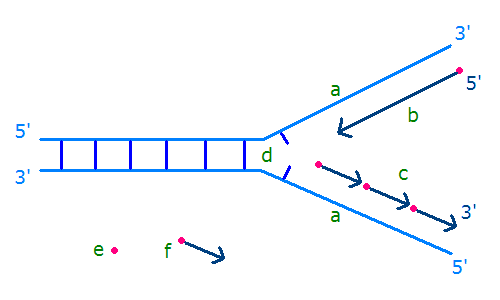
We examined the role of RNA primer–primase complexes left on the lagging ssDNA from primer synthesis in initiating early lagging-strand polymerase recycling.
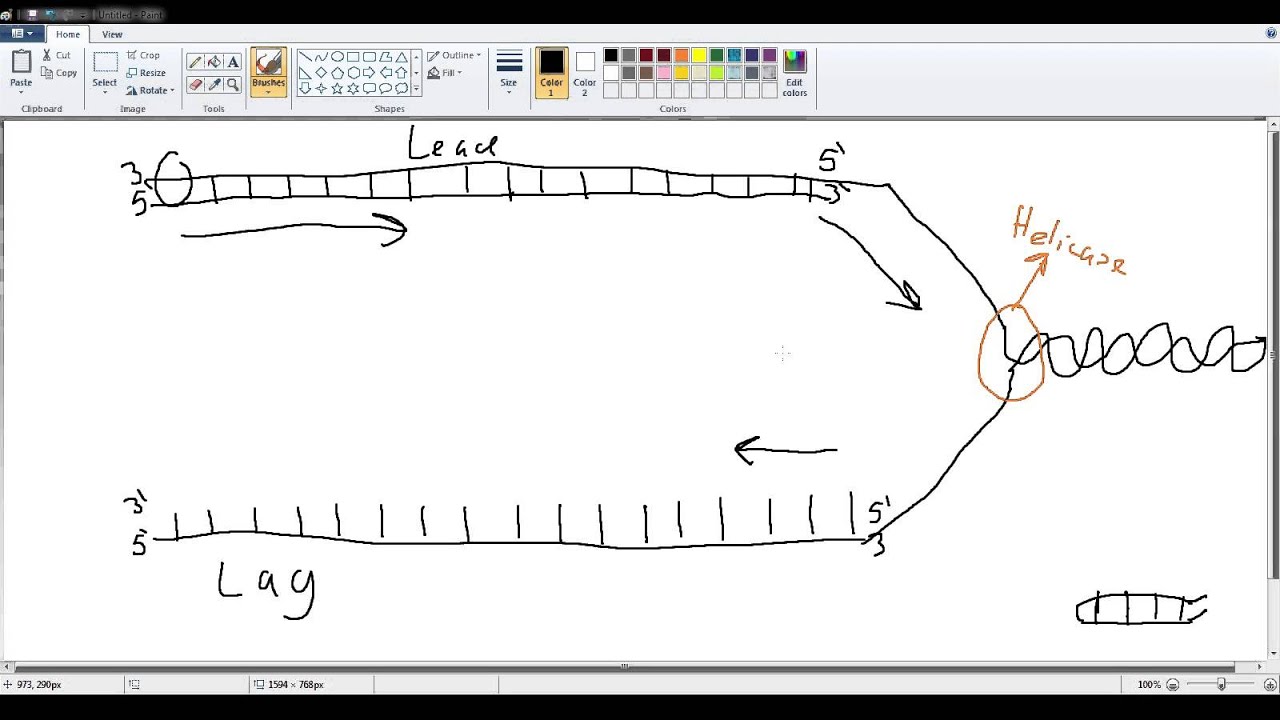
The mechanism and signal that initiate this behavior—that is, the signaling mechanism—have not been definitively identified. The lagging-strand polymerase sometimes recycles to begin the synthesis of a new Okazaki fragment before finishing the previous fragment, creating a gap between the Okazaki fragments. The opposite strand polarity of duplex DNA necessitates that the leading strand is replicated continuously whereas the lagging strand is replicated in discrete segments known as Okazaki fragments. Hanoian, Philip Gannavaram, Swathi Benkovic, Stephen J. RNA primer–primase complexes serve as the signal for polymerase recycling and Okazaki fragment initiation in T4 phage DNA replication The similarities to both bacterial and eukaryotic systems and evolutionary implications of archaeal Okazaki fragment maturation are discussed. This flap structure was cleaved by flap endonuclease 1 (Fen1) and the resultant nick was ligated by DNA ligase to form a mature lagging strand. Instead, Family B DNA polymerase (polB) was observed to rapidly fill the gaps left by polD and displaces the downstream Okazaki fragment to create a flap structure. It is shown here, however, that it stops before the previous Okazaki fragments, failing to rapidly process them. DNA polymerase D (polD) was proposed to function as the replicative polymerase in Thermococcus replicating both the leading and the lagging strands. A dual color fluorescence assay was developed to monitor reaction substrates, intermediates, and products. To address the components required for the process in Thermococcus, Okazaki fragment maturation was reconstituted in vitro using purified proteins from Thermococcus species 9°N or cell extracts. Efficient maturation prevents repeat sequence expansions, small duplications, and generation of double-stranded DNA breaks. Greenough, Lucia Kelman, Zvi Gardner, Andrew F.ĭuring replication, Okazaki fragment maturation is a fundamental process that joins discontinuously synthesized DNA fragments into a contiguous lagging strand. The Roles of Family B and D DNA Polymerases in Thermococcus Species 9°N Okazaki Fragment Maturation* The RNA trimer may, therefore, lock the complete fragment in an A-type conformation. Although the base-pair geometry, particularly in the central TATA part, is distorted, there is no evidence for a transition from the A- to the B-type conformation at the junction between RNA.DNA hybrid and DNA duplex. The fragment adopts an overall A-type conformation with 11 residues per turn.
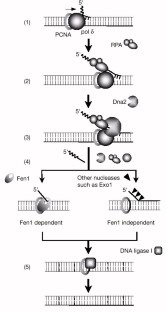
The DNA oligonucleotide d(GGGTATACGC) and the chimeric RNA-DNA oligonucleotide r(GCG)d(TATACCC) were combined to form a synthetic Okazaki fragment and its three-dimensional structure was determined by x-ray crystallography. They are composed of the growing DNA strand primed by RNA and the template strand. In DNA replication, Okazaki fragments are formed as double-stranded intermediates during synthesis of the lagging strand.
Crystal structure of an Okazaki fragment at 2-A resolutionĮgli, M.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
